Birth control can be an awkward topic to talk about, but it’s an important thing to be informed on. One of the most common forms of women’s birth control you may hear about is “the pill.” But what exactly is “the pill”?
How Does the Pill Work?
A birth control pill is a prescription oral contraceptive, meaning it is a medication prescribed by your doctor that you take by mouth to prevent pregnancy. Every pill can work a little differently. The main idea is that you take the pill daily, and the hormones in it change small aspects of your reproductive system in order to prevent pregnancy. Mainly, the bodily response to these newly introduced hormones is to stop ovulating (aka releasing the egg) and may thicken the cervical mucus to prevent sperm from reaching the egg.
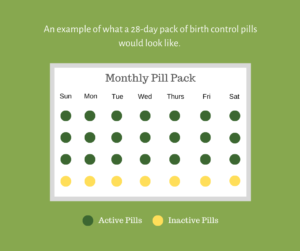
Different pills and brands may layout their pill packs differently, but generally pill packages will be made up of “active” and “inactive” pills. The active pills contain hormones, and the inactive pills do not. In general, the days you take the inactive pills would be when you have your period. Birth control pills don’t start working immediately, they do take time. Generally it’ll take 1-3 months, especially when you first start using this kind of contraceptive, to see a consistent change in your cycle and hormones. Additionally, there are different types of pills for certain menstrual issues.
What Types of Pills Are There?
There are two main types of birth control pills: combined pills, and progestin-only pills.
- Combined pills: Contain two types of hormones: estrogen and progestin. This type prevents ovulation and thickens your cervical mucus.
- Progestin-only pills: Also called “mini-pills”.These only contain the progestin hormone. These mainly thicken your cervical mucus, and thin the lining of the uterus. They may also prevent ovulation.
Why are there two types of pills?
Women’s bodies can react differently to each type of pill. Women who are more sensitive to estrogen may find the progestin-only pill to be a better fit. The progestin-only pill may also be safer for various medical conditions. Additionally, each pill is associated with different benefits. If your considering going on the pill, make sure you have a list of any medications you’re currently taking (over the counter and prescription) so that your doctor will know what kind of pill will work best for you.
Why Do People Use the Pill?
The most obvious reason people start using a birth control pill is prevention of pregnancy. If you are planning on being sexually active, this is a good way to lower your risk of getting pregnant.
By that same note, people may also use the pill to help plan their pregnancies. A couple may not be ready for a baby yet, so taking birth control until the time they are ready will help them plan ahead with more reassurance.
Those who experience extreme symptoms when on their period may simply take birth control pills to relieve those symptoms. It can help calm debilitating cramps, lighten heavy periods, and regulate irregular periods. In some cases, the use of the pill can also help clear up acne and unwanted hair growth.
What Doesn’t the Pill Do?
Taking an oral contraceptive is not a 100% guarantee. The good news is that it is about 91% effective with typical use, or 99% with perfect use. For best results, it’s important to not miss a dose, take it the same time every day, and follow the other instructions given by your doctor. This would be considered “perfect use.”
A birth control pill also does not protect against STDs–one of the other main things (besides pregnancy) you should be conscious of when sexually active. A good way to reduce your risk of contracting an STD is by using a condom. Using a condom in addition to a pill can also give you a better chance at not getting pregnant. If the pill were to fail, a condom works as backup.
The pill also does not get rid of your period: it regulates it. You should still be having your period while on the pill with the difference that it will just be more manageable.
Warnings, Side Effects, and Precautions
Are there side effects? Yes, there can be! If you’re starting the pill for the first time you can experience the following: bloating, cramps, heavy periods, shorter or longer periods, migraines, mood swings, nausea, spotting, fatigue, and more. This can be your body’s hormones reacting to the new hormones from the medication. It’s normal to experience some of these side effects. However, should you feel extreme side effects ranging anywhere from severe cramps to drastic emotional changes please call your doctor. You should never allow any medication to cause you such negative and drastic changes to your body.
As a precaution, it is important to talk with your doctor about what is best for you personally. For instance, women who have had blood clots, high blood pressure, heart or liver disease, or cancer of the breast or uterus are not recommended for the use of birth control pills. For more information or to discuss if the pill is right for you, talk to one of our doctors at any of our 3 locations.