What is Pelvic Inflammatory Disease?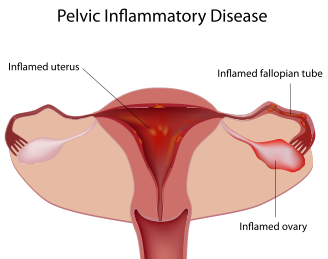
Pelvic Inflammatory Disease, also known as PID, is not a single illness. It is a broad term covering a variety of infections of the internal reproductive organs including the ovaries, fallopian tubes, uterus, ligaments supporting the uterus, and even the abdominal lining.
PID is the most common, preventable cause of infertility in the United States. It can cause scarring of the fallopian tubes which leads to blockage of the tubes and infertility.
PID is also the leading cause of ectopic pregnancy. If the fallopian tube is damaged from PID, the fertilized egg may attach to the inside wall of the tube instead of inside the uterus. An untreated ectopic pregnancy can lead to a ruptured fallopian tube, bleeding into the abdomen, and can result in death.
What are the Symptoms of Pelvic Inflammatory Disease?
Vaginal discharge is usually the first symptom to appear in women who have PID. However, a dull abdominal ache is the most common symptom and this pain may get worse with movement or sexual activity.
Some symptoms of PID include abdominal pain, abnormal uterine bleeding, fever and chills, vaginal discharge, and sometimes nausea and vomiting. However, some women do not experience any symptoms at all.
What Causes Pelvic Inflammatory Disease?
There are several bacteria that can cause PID. Neisseria gonorrhoeae and Chlamydia trachomatis are the most common. Both are sexually transmitted. The infection usually begins in the vagina, and travels through the cervix to the rest of the reproductive organs.
Gonorrhea-associated infections generally begin quickly with severe symptoms. With Chlamydia, the symptoms may be mild and develop slowly over months or even years.
Another possible cause of PID is the introduction of organisms into the reproductive tract after an induced abortion, following the birth of a child, or by the insertion of an Intrauterine Device (IUD).
What are the Risk Factors for Pelvic Inflammatory Disease?
Because the most common causes of PID are sexually transmitted, sexual activity is the largest risk factor for PID. There is a direct relationship between PID and the number of sexual partners. The more partners a woman has, the greater her risk for contracting PID.
Age is also a factor. Approximately 75% of all cases of PID occur in women under the age of 25. Younger women appear to be more susceptible to Chlamydia and gonorrhea associated infection than older women.
How is Pelvic Inflammatory Disease Treated?
Because PID is generally caused by a mixture of bacteria, your physician will probably prescribe a combination of antibiotics. Since most cases are caused by sexually transmitted diseases, your partner will need treatment as well. It is very important that you and your partner finish all the medication, even if the symptoms go away before treatment is finished. Do not have intercourse with your partner until you and your partner have completed the treatment.
It is important to see your doctor a few days after starting treatment to ensure the antibiotics are working. If your condition is not improving you may need to be hospitalized for IV antibiotics.
Resting as much as possible can help speed along your recovery. Pain medication, hot baths, or a heating pad applied to the lower back and abdomen may help relieve the discomfort of PID.